Chronic Urticaria
What is urticaria?
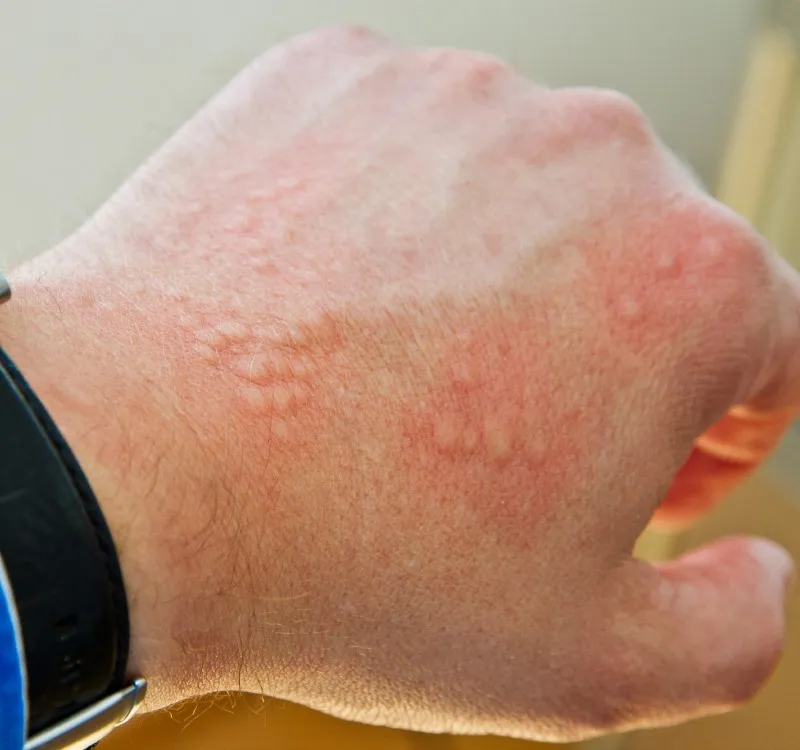
Urticaria (or hives) is an itchy, red rash that is sometimes caused by allergies. Hives are raised, red spots that range from the size of a mosquito bite to many inches in diameter. The hives may also be associated with swelling of the tissues underneath the hives.
Acute Urticaria occurs when the hives last less than six weeks, while Chronic Urticaria happens when hives last longer than six weeks.
How do I get uricaria?
Urticaria generally occurs after there is a reaction to some trigger. This reaction can release histamine, causing inflammation and itchiness.
Testing
For diagnosis of Urticaria, the physician must obtain a detailed history of the symptoms—taking special note of when and how the hives appear, how long they last, and what the hives are like.
Blood tests may also be used to help determine a diagnosis of Urticaria. The majority of testing for Urticaria is done through blood tests. Listed below are four common blood tests that are frequently used.
Complete White Blood Cell Count – This test is used to examine the levels of white blood cells to see if there may a contribution to Urticaria.
Complement Assays – This test measures the components of the Complement System to check for elevated counts that could occur within Urticaria.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate – This test analyzes how quickly red blood cells (erytrhocytes) settle within an hour. High erythrocyte sedimentation rates indicate Urticaria.
Chronic Urticaria (CU) Index – This test is used to try to detect an autoantibody that usually occurs within certain types of Urticaria

Treatment
Once a specific diagnosis is made, the physician can treat the Urticaria in several different ways, depending on the nature of the Urticaria:
-
Underlying Cause – if there is an clear underlying cause that can be treated, the physician may treat that cause of Urticaria rather than just the symptoms of Urticaria
-
Antihistamines – to reduce the itching and release of histamine that leads to hives
-
Steroids – to reduce inflammation
-
Xolair – now approved to treat difficult-to-treat Urticaria
